The freshly-released minutes from this month’s FOMC meeting suggest most members believe its may soon be appropriate to reduce the pace of rate hikes, while some officials stressed a more restrictive terminal rate should remain in place until inflation shows stronger signs of abating.
Prior to the minutes’ release, markets were pricing in a 100% chance of a half-percentage point rate hike come December, with only a 12% probability of 75 basis-point increase. Indeed, the FOMC minutes from November 2 showed most participants think the Fed should downshift its hawkish policy to perhaps a smaller, 50 basis-point hike next month, in order to avert undue risks of financial instability on the US economy. “A substantial majority of participants judged that a slowing in the pace of increase would likely soon be appropriate,” the minutes read.
“The uncertain lags and magnitudes associated with the effects of monetary policy actions on economic activity and inflation were among the reasons cited regarding why such an assessment was important,” the minutes continued. However, other participants expressed more hawkish opinions, where “ongoing increases in the target range for the federal funds rate would be appropriate in order to attain a sufficiently restrictive stance of policy to bring inflation down over time.”
At the same, the participants acknowledged that uncertainty exists in terms of how high such a restrictive territory needs to reach before the 2% inflation target is achieved, but it’ll nonetheless be based on incoming economic data. Still, participants were surprised with how wrong they were about transitory inflation, particularly that “the ultimate level of the federal funds rate that would be necessary to achieve the committee’s goals was somewhat higher than they had previously expected.”
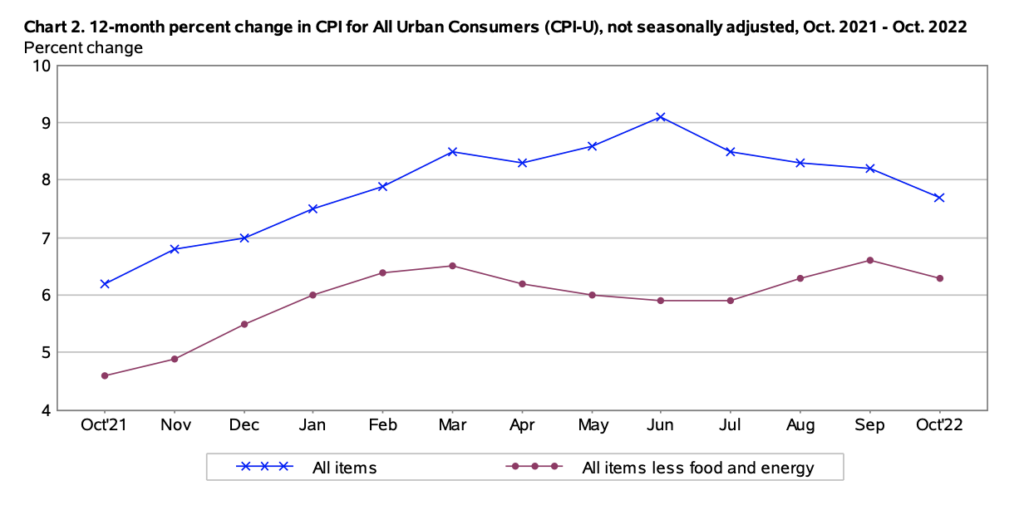
After the November meeting, Fed Chair Jerome Powell warned Americans that rates will still need to ultimately increase by more than policy makers expected during their September meeting, whilst suggesting the pace of forthcoming hikes may ease. Since the last FOMC gathering, inflation abated to an annualized 7.7%, while the unemployment rate ticked slightly higher to 3.7%— still low with respect to historic data.
Information for this briefing was found via the Federal Reserve and the BLS. The author has no securities or affiliations related to this organization. Not a recommendation to buy or sell. Always do additional research and consult a professional before purchasing a security. The author holds no licenses.