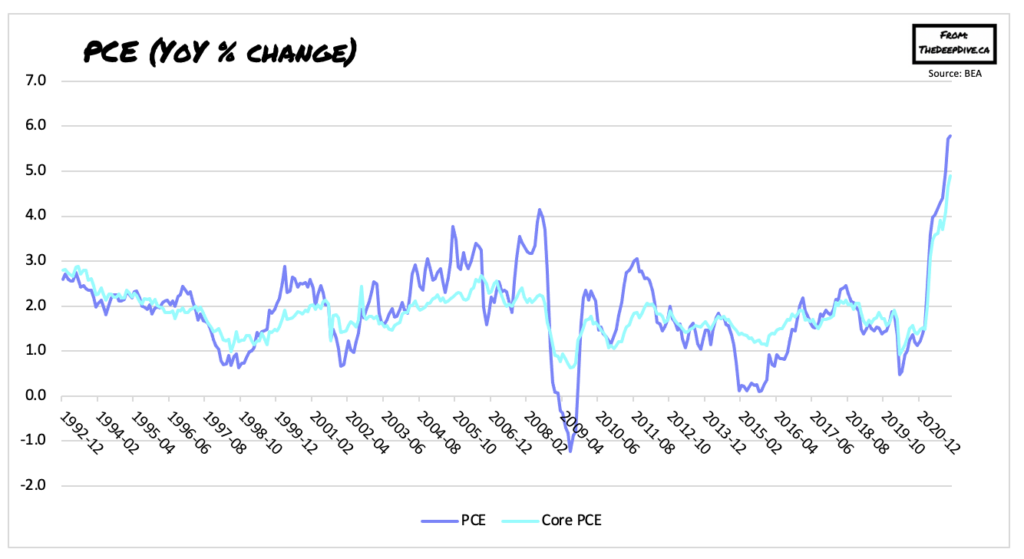
The Fed’s prized inflation indicator has not let off from scorching hot, and jumped by the most in nearly 40 years as price pressures run rampant throughout the economy.
According to latest data released by the Bureau of Economic Analysis, the personal consumption expenditures index jumped another 0.4% from the previous month to an annualized 5.8% in December, marking the sharpest increase since June 1982. Core PCE, which does not account for volatile components such as food and energy, was up 0.5% month-over-month and 4.9% higher compared to December 2021.
Alongside the inflation figures, another key concern for the Fed is the rise in employment costs, which were up substantially last quarter as businesses competed for a limited labour supply. A separate report from the Labour Department showed that the employment cost index jumped by an annual 4%, with compensation for workers in private industries rising 4.4%, including a 5% jump in salaries and wages. Those in service jobs saw their wages rise by the most, with a 6.1% increase in 2021.
The latest data comes just as the Fed prepares to aggressively tackle price pressures while maintaining a robust economic recovery. Following the completion of the FOMC’s two-day policy meeting, Fed Chair Jerome Powell announced that rate hikes will likely come as soon as March, followed by more frequent and sharper increases in borrowing costs thereafter.
Information for this briefing was found via the BLS and the sources mentioned. The author has no securities or affiliations related to this organization. Not a recommendation to buy or sell. Always do additional research and consult a professional before purchasing a security. The author holds no licenses.