On April 27, Russia decided to further escalate tensions with the West by announcing its majority state-owned energy company Gazprom would stop exporting natural gas to Poland and Bulgaria because the countries refuse to pay for the gas in Russian rubles. In late March, Russia unilaterally changed the terms of its supply contracts with “unfriendly countries” to require payment in the Russian currency.
The Russian action to force payments in rubles is part of its attempt to prop up its currency. On the surface, the strict capital controls put in place by Russia’s central bank look successful; they have lifted the ruble’s valuation back to pre-Ukraine invasion levels.
However, the currency does not trade on anything approaching a two-way or fair basis. Surging inflation in Russia and the sharp economic contraction in the country caused by Western sanctions are not reflected in the official exchange ratio.

Poland and Bulgaria fulfill 50% and 90%, respectively, of their gas requirements through Russian pipelines, yet neither country has announced any gas consumption constraints for customers. Clearly, each nation has already diversified some of its supplies. Also, the timing of the gas suspensions — the fairly moderate weather period of late April — limits the negative impact. A gas cut-off in a winter month would have had more serious implications.
European natural gas prices rallied on the news but remains far below their late February levels when Russia invaded Ukraine. On an overall basis, Gazprom supplied roughly 40% of the Europe’s natural gas needs before the war.
Dutch natural gas futures, the European benchmark — much like Henry Hub futures is the U.S. natural gas price standard — rose about 8% to 108 euros per megawatt-hour (Mwh). This price equates to a staggering US$33.44 per thousand cubic feet of gas (Mcf). By comparison, March Henry Hub gas futures closed at US$7.08 per Mcf on April 27.
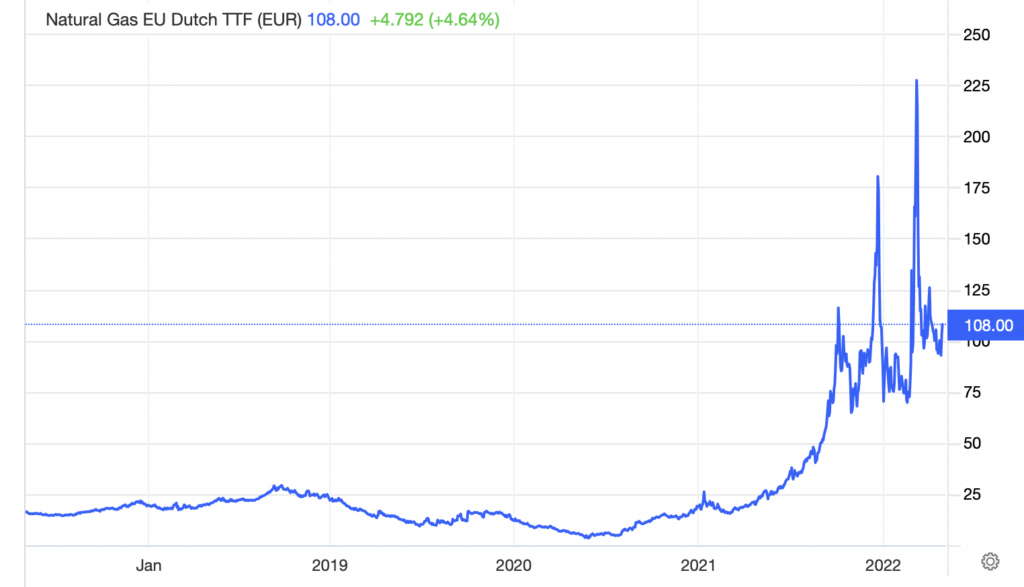
The gas market’s fairly muted reaction to the Poland/Bulgaria gas supply suspensions, versus its explosion higher on the news that the war had begun, could mean that the extraordinary natural gas prices seen about two months ago were the peak for quite some time. Nevertheless, current prices above $33/Mcf still represent an enormous burden on Europe’s consumers.
Information for this briefing was found via Edgar and the sources mentioned. The author has no securities or affiliations related to this organization. Not a recommendation to buy or sell. Always do additional research and consult a professional before purchasing a security. The author holds no licenses.